In situ hybridization ish is a powerful technique that is used to detect the localization of specific nucleic acid sequences for understanding the organization regulation and function of genes.
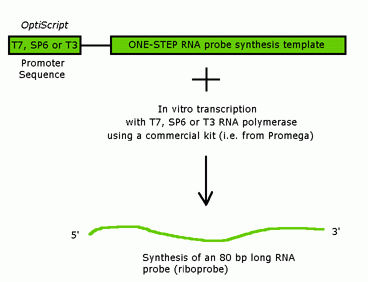
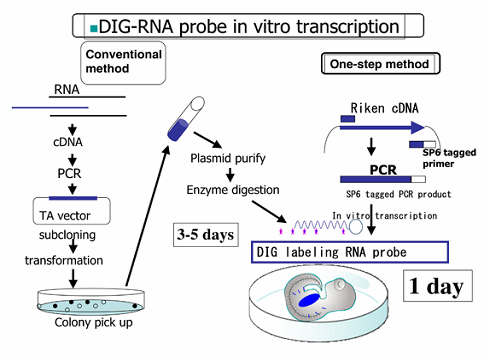
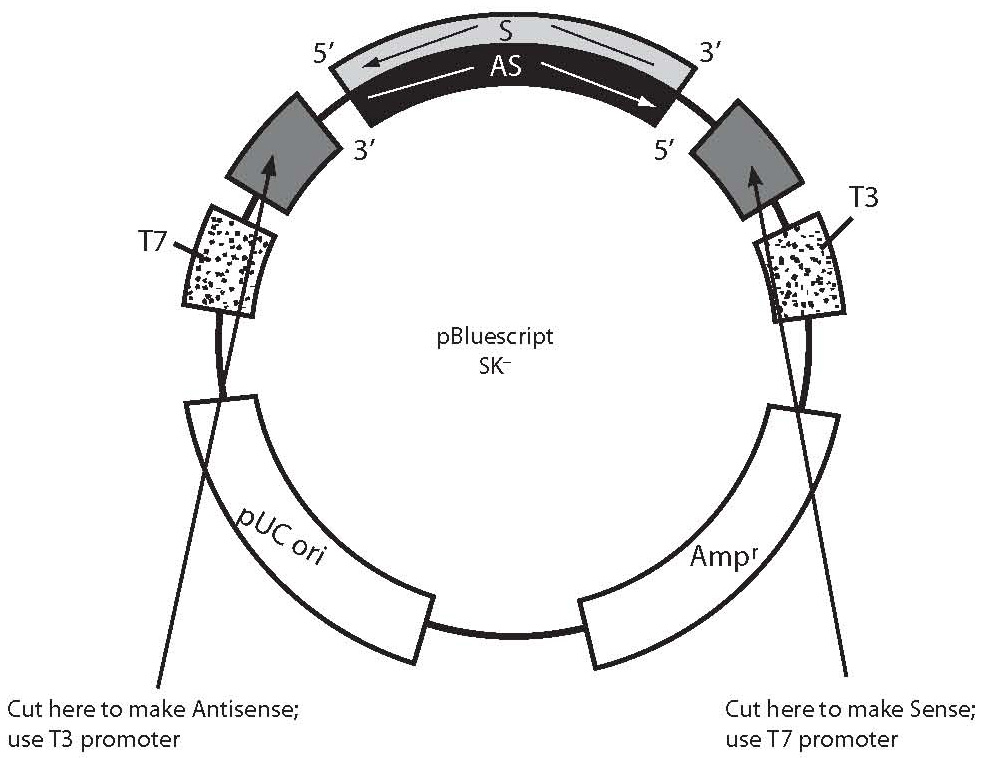
Probe synthesis for in situ hybridization.
If the gene is 2 kb the probe can be a 1 2 kb fragment of the gene.
Molecular medical microbiology second edition 2015.
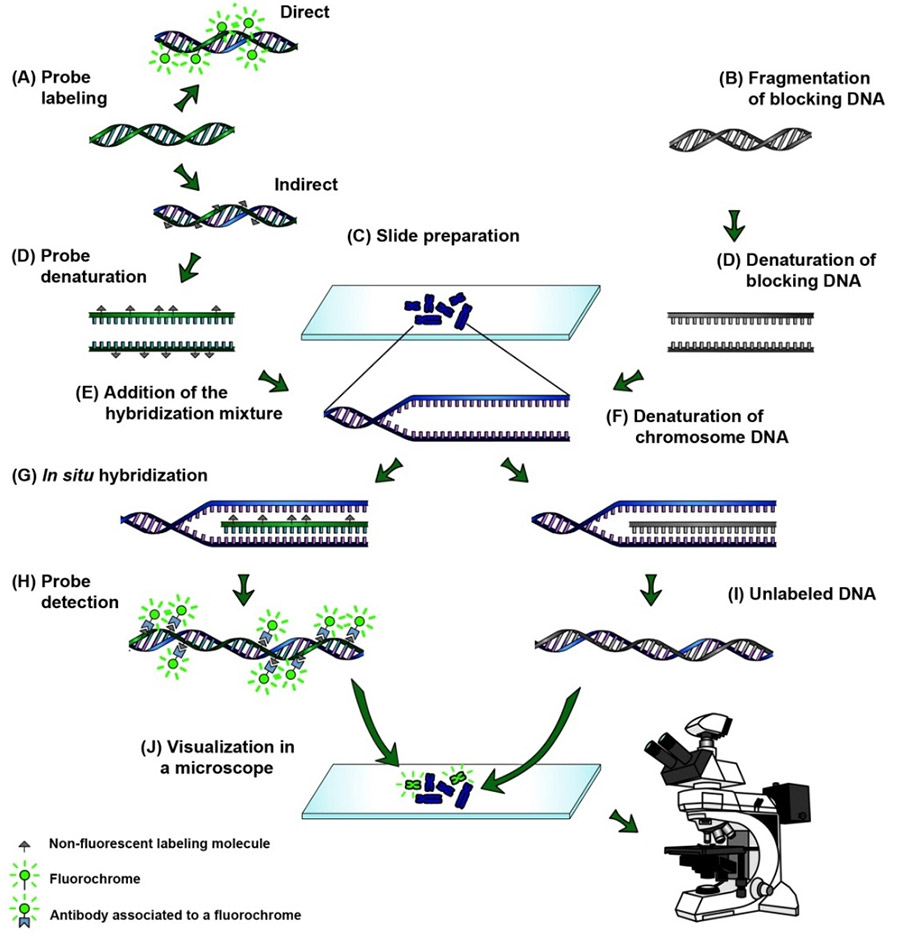
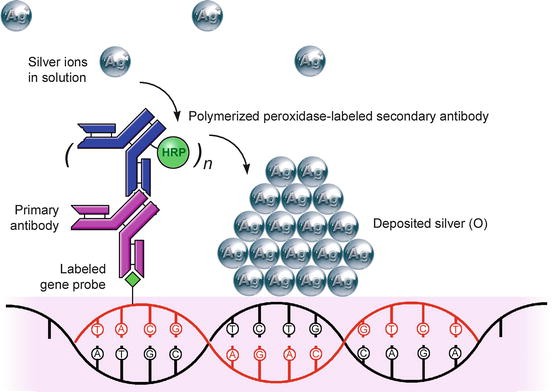
Fluorescence in situ hybridization.
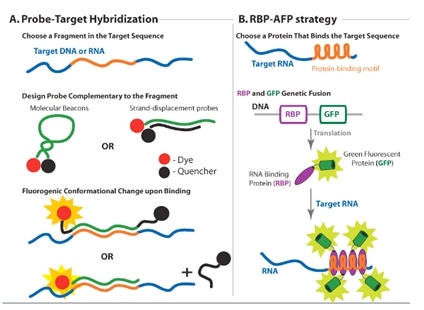
Hybridization probes use fluorescence resonance energy transfer fret technology which consists of coupling fluorescent dye pairs that have overlapping absorption and emission spectra.
Probes should be at least 1 kb.
However in most cases rna probes are obtained by in vitro transcription from plasmids containing specific promoter elements and mrna specific cdna.
10 tips for optimizing in situ hybridization here is a comprehensive list of tips for achieving high quality data by in situ hybridization a widely used biological technique providing the end user with accurate localization of endogenous bacterial or viral nucleic acids such as dna mrna and microrna in metaphase spreads cells and tissue preparations.
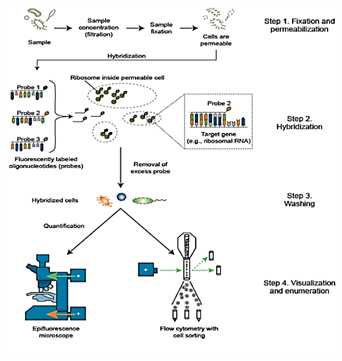
In situ hybridization ish in situ hybridization ish is a unique molecular analysis method providing accurate localization of endogenous bacterial or viral nucleic acids such as dna mrna and microrna in metaphase spreads cells and tissue preparations.
Fixation and pre treatment of samples are followed by hybridization of a labeled probe by complementary base pairing to the target and.
Select primers ideal probes are the entire length of your gene.
Most likely from contaminating fluorescein labeled nucleotides that were not incorporated into the oligonucleotide probe during synthesis.